Introduction
What is an ascending aortic aneurysm ICD 10?
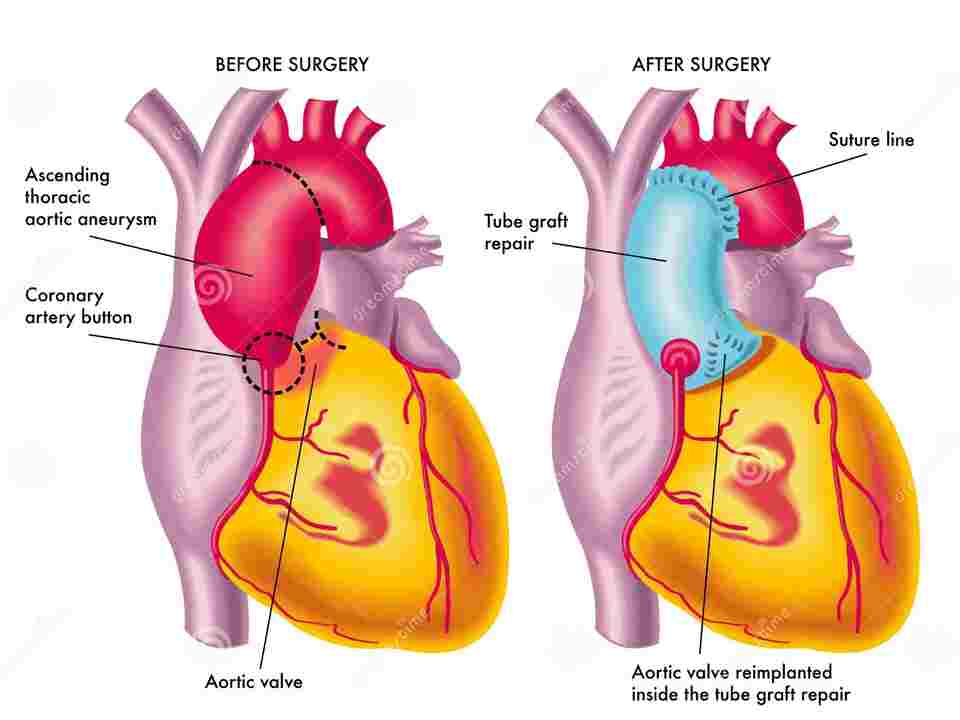
Ultimate Guide: Ascending Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10! An ascending aortic aneurysm is when the top of your heart’s main blood vessel develops a swelling (aneurysm).
If left undiagnosed and managed correctly, this enlargement can be life-threatening through complications such as aortic dissection or rupture.
Knowing how to code this condition properly with the correct ICD-10 is important for clearly documenting what you are treating, planning treatment, and insurance purposes.
This guide is intended to help you better understand ICD-10 coding for ascending aortic aneurysms icd 10 to enable medical professionals to code it correctly and effectively.
Key Takeaways
- ICD-10 Coding:
- Ensures proper patient care and treatment planning and helps in efficient medical record-keeping
- Comprehensive Knowledge:
- The specific code for ascending aortic aneurysms, icd 10, and associated illnesses need to be well-known by physicians.
- Continuing Education:
- It is necessary to continue learning and stay current with coding practices to ensure the accuracy of the documentation and treatment provided.
1: Ascending Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10 Explained
Ascending aortic aneurysm icd 10 is, after having read this article, you will know exactly what the ascending aortic aneurysm is, the dilation of the beginning part of the aorta, which is itself one main artery carrying blood from our heart to all parts of the body.
The condition can cause rupture of the aorta, either from direct infection or interaction with weakened walls that subsequently burst internally and cause massive bleeding.
What Are the Causes of Ascending Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10?
The process is multifactorial but several things that lead to the development of ascending aortic aneurysms are:
High blood pressure:
Over time, high blood pressure can weaken the walls of your aorta.
Genetic Conditions:
Disorders such as epidermolysis bullosa and Ehlers-Danlos syndrome affect connective tissues, increasing the risk of aneurysms.
Heart disease:
Cholesterol deposits in the aorta can cause narrowing and even rupture of parts of the damaged area (atherosclerosis).
Lifestyle:
A long history of smoking, bad dietary habits, and lack of physical activity are some risk factors that contribute to aneurysm development.
What are the symptoms and how was MG diagnosed?
Aortic aneurysm ascending symptoms may be mild or not present at all until complications develop. Common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Back pain
- Shortness of breath
- Cough or hoarseness
Diagnosis X-ray tests are the most common measures used to diagnose pneumothorax, and you may have one or more of these. x-rays (radiographs).
CT scan: This imaging test gives detailed images of the sizable aorta.
MRI: High-resolution images useful for monitoring aneurysms over time echocardiogram. This test uses sound waves to create a moving picture of the heart and aorta inside your chest.
Why Early Detection Matters
Hence, timely intervention is mandatory to avoid severe complications like aortic rupture or dissection. Recurrent screening and imaging for those at risk can lead to much more favorable outcomes.
2: Diagnosis of Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10 Code
The main code for ascending aortic aneurysm ICD 10 is I71.2. This code helps determine the correct categorization of the condition in medical records, which assists further when it comes to providing appropriate treatment and documentation.
What is the use of the ICD-10 code in medical records?
This ICD-10 code is then entered into the patient’s electronic records to indicate an accurate and consistent diagnosis amongst medical records. It also helps in treatment planning, insurance billing, and healthcare data analysis.
3: Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10
What is the distinction between an ascending aortic and also developing thoracic aorta?
An ascending aortic aneurysm ICD 10 is localized to the upper or ascendant portion of the aorta whereas an Ascending thoracic Aneurysm ICD10 encompasses all three compartments (ascendant/descendent) because diagnostic and treatment codes differ depending on the stage of CKD, distinguishing between each type is necessary to correctly code.
Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10
As for I71, the ICD-10 code is; ascending thoracic aortic aneurysm. 2. A precise definition of location is essential for correct treatment and follow-up.
4: ICD 10 Coding for Aneurysm Varieties
Ascending Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10 Coding for Mild
For a moderate ascending aortic aneurysm, the code is still I71.2 is used. The term “mild” describes the extent of tissue involvement (size) and a risk factor for significance — this should also be recorded in the patient’s medical record as clinical information regarding disease diagnosis.
Clinical Significance of Coding Mild Cases
For mild cases that are not eligible for surgery, of course, this can help to monitor the progression and also decide on follow-up imaging and consultations. This helps to do the risk analysis and preventive measures.
Q: How is a dilated ascending aortic aneurysm coded in ICD-10?
In this scenario, it is also coded as I71 (Dilated Ascending Aortic Aneurysm). 2. Dilated—This refers to the degree of enlargement, which is critical in deciding how urgently your dog will need treatment and whether surgery may be needed.
What Is the Treatment Burden of Dilated Ones?
More aggressive treatment with potential indications for surgery is needed and they are followed more closely to avoid rupture or dissection.
5: Onslaught Aortic Aneurysm in ICD-10 History
Syntax to indicate a history of ascending aortic aneurysm ICD 10?
An ascending aortic aneurysm in the past is documented as Z87. 891. This code is a sign of former health status that could affect their present well-being and therapy in many ways.
Why is the history document important?
History documentation is vital for knowing the patient´s medical background, appraising present risks, and helping in making good decisions during treatment.
6: Full ICD-10 Codes Listed
ICD-10 Codes Related to Ascending Aortic Aneurysms
Related ICD-10 codes
- I71. 2: Thoracic aortic aneurysm, not ruptured
- I71. 3 Abdominal aortic aneurysm rupture
- I71. 5: Abdominal aortic aneurysm, without mention of rupture
- I71. 8 aortic aneurysm of unspecified site without rupture
- I71. 9: Aortic aneurysm, unspecified11A output without rupture
| Condition | ICD-10 Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Ascending Aortic Aneurysm | I71.2 | Thoracic aortic aneurysm without rupture |
| Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (ruptured) | I71.3 | Abdominal aortic aneurysm, rupture |
| Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (unruptured) | I71.4 | Abdominal aortic aneurysm without rupture |
| Unspecified Aortic Aneurysm | I71.8 | Aortic aneurysm of the unspecified site without rupture |
| General Aortic Aneurysm | I71.9 | Aortic aneurysm, unspecified, without rupture |
So what can healthcare professionals do with these codes in everyday practice?
When these codes are used correctly, the result is accurate documentation that can be communicated between healthcare providers to better coordinate and serve patients.
Referencing these codes in context can also contribute to a more complete workup of the patient.
7: Medical Uses
How can you apply ICD-10 codes to your medical practice
ICD-10 codes help medical professionals accurately record diagnoses for better diagnosis, treatment plans, communication with insurance companies, and overall patient care.
Do you have any case examples?
Case Study 1:
A sixty-year-old man who comes several times with chest pains. Imaging shows a 4.5 cm ascending aortic aneurysm This is coded diagnosis as I71 Two, and he would be taking medication regularly to monitor and regulate his blood pressure.
Case Scenario 2:
A 70-year-old woman with a prior ascending aortic aneurysm (Z87. Is Due For A Service869 The Case Of David Ige891 Imaging findings are unchanged, but the history of PCB insertion aids in understanding this patient and subsequent potential risks.
Seeds What are Best Practices and Coding or Documentation
Accurate Documentation:
Make sure that you document the aneurysm dimensions, location, and severity in detail
Prefreshing:
Updating patient records with the latest information about a beanie-baby-dolls condition.
History Codes:
Still,, other aneurysms were also historical and these must be included to give a true representation of the patient´s health.
8: Resources and Additional Reading
Which Textbooks and Articles Should You Read?
Aortic Aneurysms:
Pathogenesis and Treatment by Reinhart Grundmann
Stuart J. Hutchison, Aorta:
Structure, Function, and Disease
WHAT ONLINE RESOURCES AND DATABASES ARE USED?
National Institutes of Health (NIH): Medical research and information.
American Heart Association (AHA):
Guidelines and educational materials on cardiovascular diseases.
ICD-10 Data:
Descriptions of ICD-10 codes, clinical modification (CM), and procedures for the public.
Continuing ED opportunities?
Online Courses:
Many institutions provide online ICD-10 coding courses.
Medical conferences and workshops: Join medical conferences that offer a live experience of how to apply the most recent coding data.
Webinars:
Join webinars held by health organizations for continuous learning.
Risk Factors for Developing an Ascending Aortic Aneurysm ICD 10 Include:
Age:
Both the risk of atherosclerosis and thoracic aortic aneurysms increase with age.
Gender:
Men are 2 to 4 times more likely to develop an ascending aortic aneurysm icd 10 than women.
Family History:
Having a family history of aortic aneurysms increases your risk.
Bicuspid Aortic Valve or Connective Tissue Disorder:
These conditions can weaken the aorta.
Heart Disease:
Conditions affecting the heart can contribute to aneurysm development.
High blood pressure:
Hypertension is a significant risk factor.
Smoking:
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) considers smoking the most significant behavioral factor linked to aortic aneurysms.
Conclusion
Why is correct ICD-10 coding of great importance when it comes to ascending aortic aneurysms?
Correct ICD-10 coding is necessary not only to support proper patient care but also for medical record keeping and treatment planning as well.
The record also assists with clear and concise communication among healthcare professionals while guiding the patient to relevant care by reporting findings based on documented conditions.
So what are medical professionals supposed to do to keep their skills fresh and coding practices up-to-date?
Medical professionals should continuously learn and get updated with the help of workshops, webinars, etc. with different standards in medical coding. Frequent re-evaluation of resources and guidelines will be important in preserving the integrity of documentation and care.
Medical Professionals can ensure they are prepared to deal with the complexities of ICD-10 coding for ascending aortic aneurysm icd 10 and manage healthcare facilities in a manner that results in improving patient outcomes by adhering to this ultimate guide.
FAQs
What is the ascending aortic aneurysm ICD 10?
The ICD-10 code for an ascending aortic aneurysm is I71.2.
How is a mild ascending aortic aneurysm ICD 10 documented?
A mild ascending aortic aneurysm is documented with the same code, I71.2, with additional notes specifying its mild nature.
What is the important history of ascending aortic aneurysm in ICD 10 coding?
Documenting the history using Z87.891 is crucial for understanding past conditions that influence current health status and treatment decisions.
What causes ascending aortic aneurysms?
Common causes include hypertension, genetic conditions, atherosclerosis, and lifestyle factors like smoking.
How can medical professionals stay updated on ICD-10 coding practices?
Medical professionals can stay updated through online courses, attending medical conferences, participating in webinars, and reviewing relevant literature.
What are the symptoms of an ascending aortic aneurysm 10?
Symptoms can include chest pain, back pain, shortness of breath, and a persistent cough or hoarseness.
How is an ascending aortic aneurysm ICD 10 diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves imaging studies such as CT scans, MRIs, and echocardiograms.
What are the treatment implications for a dilated ascending aortic aneurysm icd 10?
Dilated aneurysms often require aggressive treatment, including possible surgical intervention, and must be closely monitored.